Please Choose Your Language
Views: 222 Author: Carie Publish Time: 2025-03-11 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Introduction to Sewage Treatment
● The First Step: Primary Treatment
>> Primary Sedimentation Tanks
>> Filtration and Disinfection
● Advanced Treatment Technologies
>> Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
>> Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs)
● Environmental Impact and Sustainability
>> Water Reuse
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the purpose of primary treatment in sewage processing?
>> 2. How does secondary treatment differ from primary treatment?
>> 3. What methods are used for tertiary treatment?
>> 4. Why is pre-treatment necessary?
>> 5. What are the environmental benefits of sewage treatment?
Sewage treatment is a complex process designed to remove contaminants from wastewater, ensuring that the water released back into the environment is safe and meets regulatory standards. This process involves several stages, each crucial for effective water purification. In this article, we will delve into the first step of the sewage treatment process, exploring its significance and how it sets the stage for subsequent treatment stages.

Sewage treatment is essential for maintaining public health and environmental protection. It involves the removal of pollutants from wastewater, which includes household sewage and sometimes small amounts of industrial wastewater. The treatment process typically consists of three main stages: primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment.
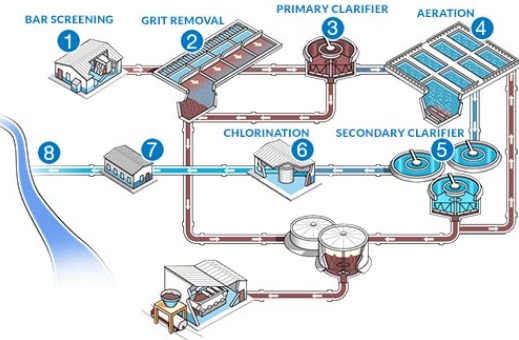
Before the main stages begin, there is a pre-treatment phase. This step involves removing large objects from the wastewater that could damage or clog pipes. Common items removed include sanitary products, nappies, plastic, leaves, and other large debris. Pre-treatment often involves physical barriers such as grates or screens to catch these items.
Illustration of Pre-Treatment Screens:
Imagine a large grid at the entrance of a wastewater treatment plant, where wastewater flows through and large debris is caught and removed. This process is crucial for preventing damage to equipment and ensuring the smooth operation of subsequent treatment stages.
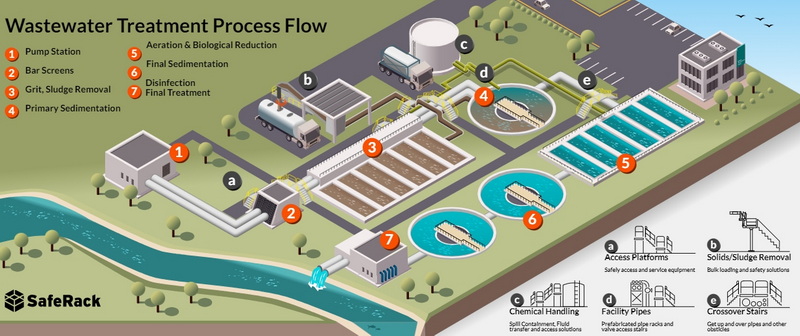
The primary treatment stage is the first major step in the sewage treatment process. It focuses on separating organic matter and sludge from the rest of the water. This is achieved by allowing the wastewater to flow through large settlement tanks, where solids sink to the bottom and grease and oils rise to the top. The oils and grease are skimmed off, and the sludge is collected and pumped away.
Primary sedimentation tanks are large, usually circular or rectangular, and are designed to hold wastewater long enough for heavy solids to settle to the bottom. This process is also known as primary clarification. The sludge collected at the bottom is called primary sludge, while the floating material, such as grease and oils, is skimmed off the surface.
Illustration of Primary Sedimentation Tanks:
Imagine a large tank where wastewater flows in and is held for a period, allowing solids to settle and oils to float. This process is crucial for removing large particles and reducing the load on subsequent treatment stages.
Following primary treatment, the wastewater moves to the secondary treatment stage. This stage involves biological processes that further break down organic matter. The wastewater is placed in aeration tanks where bacteria and other microorganisms feed on the remaining pollutants, converting them into carbon dioxide, water, and biomass.
Aeration tanks are designed to provide an aerobic environment, where air is pumped into the water to encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria. This process is known as activated sludge treatment. The bacteria consume organic pollutants, significantly reducing the biological oxygen demand (BOD) of the wastewater.
Illustration of Aeration Tanks:
Picture a rectangular tank filled with wastewater, where air bubbles are continuously pumped in to support the growth of bacteria. This process is vital for breaking down organic pollutants.
The tertiary treatment stage is the final step in the sewage treatment process. It involves further purification of the wastewater to remove any remaining pollutants, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, and to disinfect the water. This stage may include processes like filtration through sand and charcoal beds or chemical treatment.
In this stage, the water is filtered to remove any remaining inorganic substances and pathogens. Disinfection methods, such as chlorination or UV light treatment, are used to kill bacteria and viruses, ensuring the water is safe for release into the environment.
Illustration of Tertiary Treatment:
Imagine a tank filled with sand and charcoal, where wastewater flows through, removing any remaining impurities. This step is crucial for producing high-quality water that can be safely discharged.
In addition to the traditional stages, advanced technologies are being integrated into sewage treatment processes. These include membrane bioreactors (MBRs), which combine biological treatment with membrane filtration to produce high-quality effluent. Another technology is advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), which use chemical oxidants to break down persistent organic pollutants.
MBRs are systems that use membranes to separate treated water from the biological sludge. They offer high-quality effluent and can be more efficient in terms of space and energy compared to traditional activated sludge systems.
Illustration of MBR Systems:
Picture a system where wastewater flows through a membrane, separating clean water from sludge. This technology is becoming increasingly popular due to its efficiency and ability to produce high-quality water.
AOPs involve the use of oxidizing agents like ozone or hydrogen peroxide to break down organic pollutants. These processes are effective against a wide range of contaminants, including those resistant to biological treatment.
Illustration of AOPs:
Imagine a system where chemical oxidants are added to wastewater to break down persistent pollutants. This technology is particularly useful for treating industrial wastewater with complex contaminants.
Sewage treatment plays a critical role in environmental sustainability. By removing pollutants from wastewater, treatment plants help protect aquatic ecosystems and maintain water quality. Additionally, treated wastewater can be reused for irrigation, toilet flushing, and other non-potable purposes, reducing the demand on freshwater resources.
Water reuse is becoming increasingly important as a strategy to conserve water resources. Treated wastewater can be safely used for various purposes, reducing the strain on natural water sources.
Illustration of Water Reuse:
Picture a system where treated wastewater is piped to a golf course for irrigation. This practice not only conserves water but also reduces the environmental impact of wastewater discharge.
The first step in the sewage treatment process, primary treatment, is crucial for removing large solids and oils from wastewater. This stage sets the foundation for subsequent biological and chemical treatments, ensuring that the final effluent is safe for environmental discharge. Understanding each stage of the treatment process highlights the complexity and importance of wastewater management in maintaining public health and environmental sustainability.
The primary treatment stage is designed to remove large solids and oils from wastewater, reducing the load on subsequent treatment stages and preventing damage to equipment.
Secondary treatment involves biological processes that break down organic pollutants using bacteria, whereas primary treatment focuses on physical separation of solids.
Tertiary treatment may include filtration through sand and charcoal beds, chemical treatment, or disinfection methods like chlorination or UV light to remove remaining pollutants and pathogens.
Pre-treatment is necessary to remove large objects that could damage pipes or interfere with the treatment process, ensuring that the wastewater can be effectively processed.
Sewage treatment helps protect water bodies by removing pollutants that could harm aquatic life and human health, ensuring that discharged water meets environmental standards.
This article highlights the top stannous sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in the UK, focusing on their product quality, industrial applications, and market presence. It emphasizes the UK's strength in producing high-purity stannous sulfate for surface treatment, water treatment, and electroplating industries. Key players like REAXIS and Atotech lead the market with innovative solutions, while OEM support and regulatory compliance remain core advantages of UK suppliers. The article also addresses the compound's uses and includes a detailed FAQ to assist industry professionals.
Germany leads Europe in Stannous Sulfate manufacturing, supplying high-purity, reliable chemicals essential for electroplating, glass production, pharmaceuticals, and more. Key German suppliers like TIB Chemicals AG, MCC Menssing, Univar Solutions GmbH, and VMP Chemiekontor GmbH offer tailored solutions, strict quality control, and global distribution for diverse industrial demands.
This article explores the top stannous sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in Europe, highlighting leading companies like TIB Chemicals and Chimica Panzeri. It details production technologies, quality standards, industry applications, and OEM services, offering insights for markets requiring high-purity stannous sulfate chemicals.
This article explores the top stannous sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in France, highlighting their product quality, compliance with environmental standards, customized OEM services, and key industrial applications such as aluminum surface treatment, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater management.
This article explores the top stannous sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in America, detailing key companies, product forms, industries served, manufacturing processes, quality controls, and environmental considerations. It highlights the benefits of sourcing stannous sulfate locally with customization and technical support options. Insightful images illustrate stannous sulfate forms, production, and applications in industrial processes. Finally, a FAQ section addresses common queries related to stannous sulfate use and supply.
This comprehensive report explores Japan's top nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers, highlighting their production capabilities, market positions, and product applications. Featuring companies like Sumitomo Metal Mining and SEIDO Chemical Industry, the article delves into manufacturing processes, industry uses, and environmental practices, reflecting the pivotal role of Japanese firms in the advancing global nickel sulfate market.
South Korea is a leading global hub for nickel sulfate manufacturing, dominated by Korea Zinc and KEMCO with a combined annual capacity of 80,000 tons. Leveraging advanced smelting technologies and government-supported strategic status, these manufacturers supply high-quality nickel sulfate for electric vehicle batteries, surface treatment, and chemical industries. South Korean suppliers offer comprehensive OEM services to international clients, meeting growing global demand with innovation, sustainability, and quality.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of leading nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in Portugal, covering their technological capabilities, product lines, market roles, and strict compliance with international standards. Highlighting diverse applications from electroplating to battery manufacturing, it showcases Portugal’s growing importance in the global nickel sulfate supply chain. Accompanied by relevant images, the article emphasizes sustainability, innovation, and quality as cornerstones of the Portuguese chemical sector.
This article explores the top nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in Spain, highlighting their product offerings, quality standards, and strategic advantages. It covers Spanish industry applications, OEM services, and explains why Spain is a preferred sourcing hub for global chemical buyers. The article also includes detailed FAQs and relevant images to provide a comprehensive understanding of the nickel sulfate market in Spain.
Italy’s nickel sulfate manufacturing and supply chain is advanced, diverse, and globally integrated—supporting key industries like batteries, electroplating, and catalysts. With leading companies, customized services, and sustainable practices, Italian nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers are crucial to meeting the world’s growing demand for this essential chemical.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the top nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in Russia, focusing on major companies like Norilsk Nickel, their production processes, market presence, environmental initiatives, and the diverse industrial applications of nickel sulfate. It serves as a valuable resource for international businesses looking to source high-quality nickel sulfate from Russia.
Aluminum alloys have become indispensable materials in modern industry, owing to their light weight, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, workability, and versatility. However, their durability—especially when used in challenging environments—is critically dependent on
Electrophoretic coatings, often referred to as *E-coatings* or *electrophoretic deposition (EPD)*, have revolutionized surface finishing in the modern manufacturing landscape. They blend chemistry, material science, and advanced technology to create coatings that are durable, uniform, and environmen
Discover Europe's most prominent Nickel Sulfate Manufacturers and Suppliers, including sustainability-focused innovators and rapid-response distributors serving the EV, electroplating, and advanced materials sectors. Learn about top companies, key trends, market drivers, and FAQs to inform your industrial chemical sourcing decisions. This comprehensive guide highlights the critical role nickel sulfate plays in Europe’s green industrial future.
This article details France’s leading role in nickel sulfate production, covering major manufacturers and suppliers, innovative production methods, sustainability commitments, and the industry’s critical role in green technology supply chains. It also examines market drivers, regulatory compliance, and supply chain strategies while answering common industry questions. The content is especially relevant for businesses seeking OEM solutions for aluminum profile treatment and battery production.
This comprehensive guide details the leading Nickel Sulfate Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany, highlighting their strengths, product applications, and why Germany is a global leader. It covers selection criteria, market trends, and answers to key FAQs for buyers and industry professionals.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to the UK’s top Nickel Sulfate Manufacturers and Suppliers, highlighting industry applications, leading brands, and sourcing strategies in the rapidly growing British and global markets. From surface finishing to electric vehicle batteries, discover how to select the right partner and stay ahead of industry shifts.
This article explores the top Nickel Sulfate Manufacturers and Suppliers in America, highlighting their key products, application areas, and essentials of reliable sourcing. With detailed industry profiles, market trends, future outlooks, and FAQs, it serves as a vital comprehensive resource for businesses seeking high-quality nickel sulfate and dependable partnership.
Choosing the best chemical raw materials for aluminum profiles is **critical to ensuring strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and sustainability** in the final products. The selection impacts not only the mechanical and aesthetic qualities but also influences cost-effectiveness, production ef
In the global industrial landscape, **chemical raw materials for surface treatment** play a critically transformative role in enhancing the durability, functionality, and aesthetics of countless products. Surface treatment chemicals help prevent corrosion, improve adhesion, increase wear resistance,
