Please Choose Your Language
Views: 222 Author: Carie Publish Time: 2025-03-10 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Introduction to Modern Sewage Treatment Plants
>> Advanced Biological Treatment Processes
● Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
>> Composting
● Green Infrastructure and Public Awareness
● Environmental and Economic Benefits
>> Water Reuse and Conservation
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the key features of modern sewage treatment plants?
>> 2. How do modern sewage treatment plants contribute to sustainability?
>> 3. What role does IoT play in modern sewage treatment plants?
>> 4. How do modern sewage treatment plants manage sludge?
>> 5. What are the economic benefits of modern sewage treatment plants?
Modern sewage treatment plants have evolved significantly over the years, incorporating advanced technologies and sustainable practices to ensure efficient wastewater management. These facilities not only treat wastewater but also contribute to environmental protection and resource conservation. In this article, we will explore the key features, technologies, and benefits of modern sewage treatment plants.

Modern sewage treatment plants are designed with a focus on energy efficiency, sustainability, and advanced biological treatment processes. They utilize technologies such as the Activated Sludge process, Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR), Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBR), and Membrane Bioreactors (MBR) to ensure high-quality water treatment.
These processes are crucial for removing organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus from wastewater, making the treated water suitable for reuse in non-potable applications like irrigation and industrial processes.
Modern plants often incorporate renewable energy sources such as solar power, wind energy, or biogas generated from anaerobic digestion of sludge. This not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes the plant's carbon footprint.
- Solar Power: Many modern sewage treatment plants use solar panels to generate electricity, reducing their reliance on non-renewable energy sources. Solar power can be used to operate pumps, aerators, and other equipment within the plant.
- Biogas from Anaerobic Digestion: Sludge, a byproduct of wastewater treatment, is processed through anaerobic digestion to produce biogas, which can be used as a renewable energy source or converted into biofertilizers. This process not only reduces waste but also provides a sustainable energy solution.
Advanced monitoring and control systems are integral to modern sewage treatment plants. These systems use real-time data analytics and remote-control capabilities to optimize the treatment process, ensure compliance with regulations, and reduce operational costs.
IoT devices are strategically placed throughout the plant to collect data on water quality and treatment efficiency. This data is transmitted to a central platform for analysis, enabling prompt adjustments to the treatment process as needed. Real-time monitoring helps in detecting anomalies early, preventing potential environmental hazards.
Sludge, a byproduct of wastewater treatment, is treated using processes like anaerobic digestion or composting. These methods not only reduce waste but also produce valuable resources such as biogas and biofertilizers.
Anaerobic digestion is a process where microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas (a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide) and a nutrient-rich sludge that can be used as fertilizer. This process is highly efficient in reducing the volume of sludge and generating renewable energy.
Composting involves the aerobic decomposition of organic materials, resulting in a stable, humus-like product that can be used as a soil conditioner. This method is particularly effective for managing sludge from smaller treatment plants or in regions where anaerobic digestion facilities are not available.
Modern plants implement various odor control methods to minimize unpleasant smells from the treatment process. These methods include chemical treatment, biofiltration, and scrubbing systems.
Biofiltration involves passing air through a bed of microorganisms that break down odor-causing compounds, effectively reducing the smell. This method is environmentally friendly and cost-effective compared to chemical treatments.

Modern sewage treatment plants often incorporate green infrastructure elements like constructed wetlands or bioswales to manage stormwater runoff and enhance ecological sustainability. Additionally, they emphasize public awareness and education about proper wastewater management and water conservation.
Constructed wetlands are artificial ecosystems designed to mimic natural wetlands. They help in filtering stormwater runoff and improving water quality. These systems also provide habitats for wildlife, enhancing biodiversity.
Public education programs are crucial for promoting awareness about the importance of wastewater management and water conservation. These programs often include workshops, tours of treatment facilities, and community outreach initiatives to engage the public in sustainable practices.
Investing in modern sewage treatment plants offers several environmental and economic advantages. They reduce the release of harmful pollutants into water bodies, promote water reuse and conservation, and provide cost-effective operations through automation and energy efficiency.
Advanced filtration and disinfection processes enable the production of high-quality treated water that can be reused for non-potable purposes, contributing to water conservation, especially in regions facing water scarcity. Water reuse can significantly reduce the demand on potable water resources, supporting sustainable development.
The economic benefits of modern sewage treatment plants include reduced operational costs through energy efficiency and automation, revenue generation from the sale of biogas and biofertilizers, and job creation in the wastewater management sector. Additionally, these plants contribute to economic growth by supporting industries that rely on treated water for operations.
As technology continues to evolve, future sewage treatment plants are likely to incorporate even more advanced technologies such as nanofiltration, advanced oxidation processes, and artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance. These advancements will further enhance efficiency, sustainability, and environmental protection.
Nanofiltration is a membrane filtration process that can remove dissolved solids and other contaminants from water, producing high-quality treated water suitable for various applications. This technology is particularly promising for regions requiring stringent water quality standards.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be integrated into sewage treatment plants to predict maintenance needs, optimize treatment processes, and detect anomalies in real-time. AI-driven systems can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Modern sewage treatment plants are designed to be efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly. They incorporate advanced technologies, renewable energy sources, and innovative management practices to ensure high-quality wastewater treatment while minimizing environmental impact. As urbanization continues to grow, the role of these plants in maintaining public health and environmental sustainability will become increasingly important.
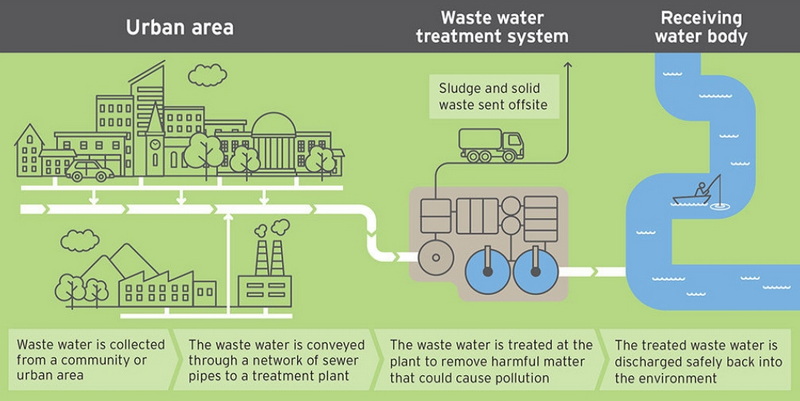
Modern sewage treatment plants feature advanced biological treatment processes, energy efficiency through renewable energy sources, advanced monitoring and automation systems, effective sludge management, and odor control measures. They also emphasize public awareness and incorporate green infrastructure for sustainability.
Modern sewage treatment plants contribute to sustainability by using renewable energy sources like solar power and biogas, reducing waste through effective sludge management, and promoting water reuse and conservation. They also minimize environmental impact by reducing pollutant discharge into water bodies.
IoT plays a crucial role in modern sewage treatment plants by enabling real-time monitoring of water quality and treatment efficiency. IoT devices collect data that is used to optimize the treatment process, detect illegal discharges, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Modern sewage treatment plants manage sludge through processes like anaerobic digestion and composting. These methods reduce waste and produce valuable resources such as biogas and biofertilizers, contributing to energy efficiency and sustainability.
Modern sewage treatment plants offer economic benefits through cost-effective operations. Automation and energy efficiency reduce operational costs, while the production of biogas and biofertilizers provides additional revenue streams. They also promote water reuse, which can reduce the need for potable water in non-potable applications.
This article highlights the top stannous sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in the UK, focusing on their product quality, industrial applications, and market presence. It emphasizes the UK's strength in producing high-purity stannous sulfate for surface treatment, water treatment, and electroplating industries. Key players like REAXIS and Atotech lead the market with innovative solutions, while OEM support and regulatory compliance remain core advantages of UK suppliers. The article also addresses the compound's uses and includes a detailed FAQ to assist industry professionals.
Germany leads Europe in Stannous Sulfate manufacturing, supplying high-purity, reliable chemicals essential for electroplating, glass production, pharmaceuticals, and more. Key German suppliers like TIB Chemicals AG, MCC Menssing, Univar Solutions GmbH, and VMP Chemiekontor GmbH offer tailored solutions, strict quality control, and global distribution for diverse industrial demands.
This article explores the top stannous sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in Europe, highlighting leading companies like TIB Chemicals and Chimica Panzeri. It details production technologies, quality standards, industry applications, and OEM services, offering insights for markets requiring high-purity stannous sulfate chemicals.
This article explores the top stannous sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in France, highlighting their product quality, compliance with environmental standards, customized OEM services, and key industrial applications such as aluminum surface treatment, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater management.
This article explores the top stannous sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in America, detailing key companies, product forms, industries served, manufacturing processes, quality controls, and environmental considerations. It highlights the benefits of sourcing stannous sulfate locally with customization and technical support options. Insightful images illustrate stannous sulfate forms, production, and applications in industrial processes. Finally, a FAQ section addresses common queries related to stannous sulfate use and supply.
This comprehensive report explores Japan's top nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers, highlighting their production capabilities, market positions, and product applications. Featuring companies like Sumitomo Metal Mining and SEIDO Chemical Industry, the article delves into manufacturing processes, industry uses, and environmental practices, reflecting the pivotal role of Japanese firms in the advancing global nickel sulfate market.
South Korea is a leading global hub for nickel sulfate manufacturing, dominated by Korea Zinc and KEMCO with a combined annual capacity of 80,000 tons. Leveraging advanced smelting technologies and government-supported strategic status, these manufacturers supply high-quality nickel sulfate for electric vehicle batteries, surface treatment, and chemical industries. South Korean suppliers offer comprehensive OEM services to international clients, meeting growing global demand with innovation, sustainability, and quality.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of leading nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in Portugal, covering their technological capabilities, product lines, market roles, and strict compliance with international standards. Highlighting diverse applications from electroplating to battery manufacturing, it showcases Portugal’s growing importance in the global nickel sulfate supply chain. Accompanied by relevant images, the article emphasizes sustainability, innovation, and quality as cornerstones of the Portuguese chemical sector.
This article explores the top nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in Spain, highlighting their product offerings, quality standards, and strategic advantages. It covers Spanish industry applications, OEM services, and explains why Spain is a preferred sourcing hub for global chemical buyers. The article also includes detailed FAQs and relevant images to provide a comprehensive understanding of the nickel sulfate market in Spain.
Italy’s nickel sulfate manufacturing and supply chain is advanced, diverse, and globally integrated—supporting key industries like batteries, electroplating, and catalysts. With leading companies, customized services, and sustainable practices, Italian nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers are crucial to meeting the world’s growing demand for this essential chemical.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the top nickel sulfate manufacturers and suppliers in Russia, focusing on major companies like Norilsk Nickel, their production processes, market presence, environmental initiatives, and the diverse industrial applications of nickel sulfate. It serves as a valuable resource for international businesses looking to source high-quality nickel sulfate from Russia.
Aluminum alloys have become indispensable materials in modern industry, owing to their light weight, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, workability, and versatility. However, their durability—especially when used in challenging environments—is critically dependent on
Electrophoretic coatings, often referred to as *E-coatings* or *electrophoretic deposition (EPD)*, have revolutionized surface finishing in the modern manufacturing landscape. They blend chemistry, material science, and advanced technology to create coatings that are durable, uniform, and environmen
Discover Europe's most prominent Nickel Sulfate Manufacturers and Suppliers, including sustainability-focused innovators and rapid-response distributors serving the EV, electroplating, and advanced materials sectors. Learn about top companies, key trends, market drivers, and FAQs to inform your industrial chemical sourcing decisions. This comprehensive guide highlights the critical role nickel sulfate plays in Europe’s green industrial future.
This article details France’s leading role in nickel sulfate production, covering major manufacturers and suppliers, innovative production methods, sustainability commitments, and the industry’s critical role in green technology supply chains. It also examines market drivers, regulatory compliance, and supply chain strategies while answering common industry questions. The content is especially relevant for businesses seeking OEM solutions for aluminum profile treatment and battery production.
This comprehensive guide details the leading Nickel Sulfate Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany, highlighting their strengths, product applications, and why Germany is a global leader. It covers selection criteria, market trends, and answers to key FAQs for buyers and industry professionals.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to the UK’s top Nickel Sulfate Manufacturers and Suppliers, highlighting industry applications, leading brands, and sourcing strategies in the rapidly growing British and global markets. From surface finishing to electric vehicle batteries, discover how to select the right partner and stay ahead of industry shifts.
This article explores the top Nickel Sulfate Manufacturers and Suppliers in America, highlighting their key products, application areas, and essentials of reliable sourcing. With detailed industry profiles, market trends, future outlooks, and FAQs, it serves as a vital comprehensive resource for businesses seeking high-quality nickel sulfate and dependable partnership.
Choosing the best chemical raw materials for aluminum profiles is **critical to ensuring strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and sustainability** in the final products. The selection impacts not only the mechanical and aesthetic qualities but also influences cost-effectiveness, production ef
In the global industrial landscape, **chemical raw materials for surface treatment** play a critically transformative role in enhancing the durability, functionality, and aesthetics of countless products. Surface treatment chemicals help prevent corrosion, improve adhesion, increase wear resistance,
